Table of Contents
3.1.b (viii) Stateful, stateless DHCPv6
Stateless:
SLAAC and DHCPv6 can go hand in hand because SLAAC does not disseminate other information like DNS or other DHCP options.
These are things that we no longer necessarily have to track so they can be stateless. However they still require a DHCPv6 server for.
For example here’s a config of DHCPv6 just for domain and dns, which is a common configuration you might implement.
en conf t ipv6 dhcp pool DHCPPOOL dns-server 2000::9999:1 domain-name mydomain.com interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ipv6 address 2000::9999:1/64 ipv6 nd other-config-flag ipv6 dhcp server DHCPPOOL
SLAAC will give us the address, while DHCPv6 will give us the domain info.
We can use the other-config-flag or the managed-config-flag
In the above example we used the other-config-flag in our configuration, this tells the host use the DHCPv6 server only for dhcp options, but not the IP.
Managed-config-flag tells the host to use the DHCPv6 server for both addressing and options.
So now what happens when a host comes on the network?
Here is the process:
1. The host will send out a router solicitation
2. R1 will respond with a router advertisement indicating the flags (other configuration) and the prefix to use via SLAAC
3. The host will utilize SLAAC for the address and then initiate another proceess for the DHCPv6 DNS options
Here is the flag in the Router advertisement from R1 to the client
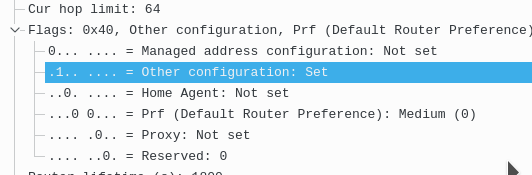
Here is the bottom of the same packet telling him what prefix to use
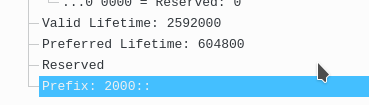
Now the client will send out a DHPc6 request for DNS
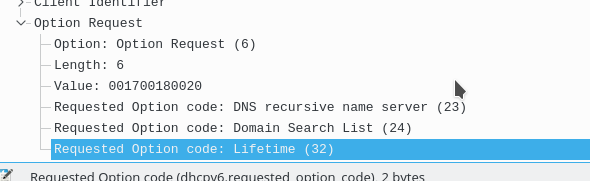
Finally R1 will reply with DNS info
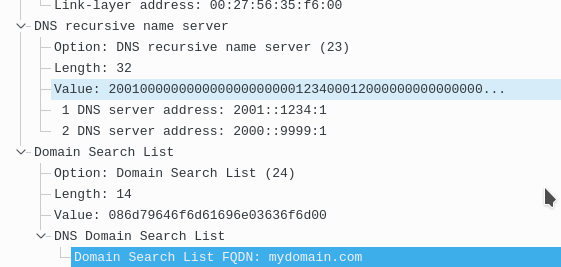
Stateful:
Of course we can use DHCPv6 to distribute and track everything, here’s how that’s configured on a Cisco router:
en conf t ipv6 dhcp pool DHCPPOOL address prefix 2000:9999::/64 lifetime infinite infinite link-address 2000:9999::227:56FF:FE35:F601/64 dns-server 2000:9999::227:56FF:FE35:F601 domain-name mylab.com int g0/1 ipv6 dhcp server DHCPPOOL ipv6 add 2000:9999::/64 eui-64 no shut
The client connected to the lan then just needs:
int g0/1 ipv6 address dhcp ipv6 enable
As described in 3.1.b (vi) then the DHCPv6 process starts which is : solicit, advertise, request, reply

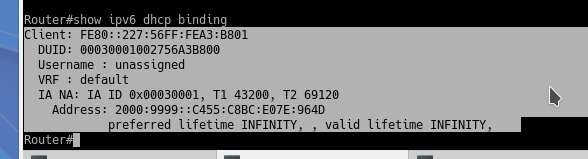
Some verification commands for IPv6 DHCP include:
A general overview of the DHCP config:
show ipv6 dhcp pool <poolname>
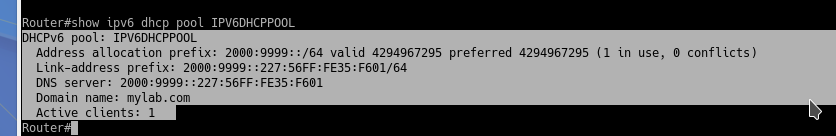
Information about each DHCP client:
show ipv6 dhcp binding