Table of Contents
3.1.b (iii) ND, RS/RA
IPv6 address resolution.
In IPv4 we had arp, to facilitate layer 2 communication. In IPv6 we have ICMPv6 neighbor discovery (ND).
The neighbor discovery protocol has two purposes:
1. For discovering and tracking other IPv6 hosts
2. For automatic address configuration
ND uses 5 ICMPv6 messages.
neighbor solicitation
neighbor advertisement
router solicitation
router advertisement
neighbor redirect
Neighbor advertisements:


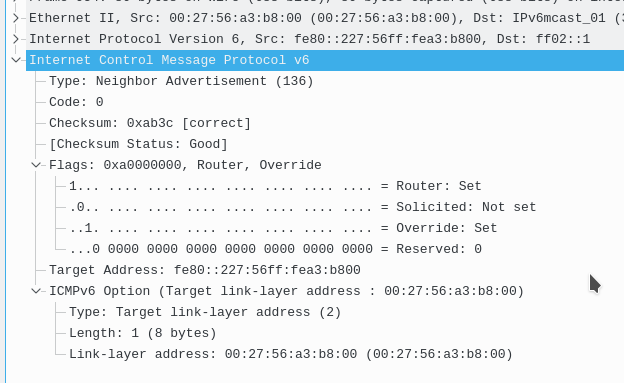
This ICMP message features 6 fields:
Type: Neighbor advertisement (136)
Code: 0
Checksum
flags:
Target address:
ICMP v6 options
IPv6 hosts send neighbor advertisements (NA) often to let others know that they are on the network. (equivalent to ARP response or gratuitous arp)
Neighbor solicitation:


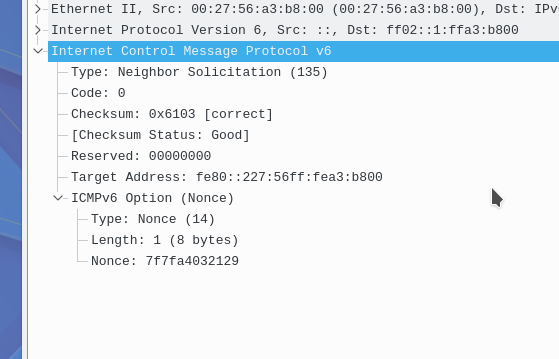
This ICMPv6 message features 6 fields:
Type : Neighbor solicitation (135)
Code : 0
Checksum:
Reserved:
Target address:
ICMP v6 options
IPv6 hosts send neighbor solicitations (NS), these have 3 purposes:
verifying neighbor reachability
layer 3 to layer 2 address resolution (the ARP request equivalent)
and
Detecting duplicate addresses
Duplicate address detection or DAD is done by the neighbor solicitation message. When a host configures itself with any address, whether it be link local or global via SLAAC, it will use a neighbor solicitation message to check if the address is already in use. The message sourced from when doing DAD is “::”, this address is also called the unspecified address.
Router advertisements:


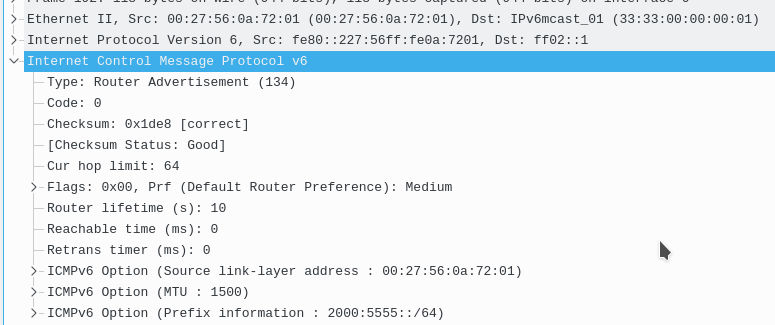

The router advertisement features 11 fields, some which have more sub fields.
All of the parent fields (and most common fields) are:
Type: Router advertisement (134)
Code: 0
Checksum
Cur hop limit : 64
Flags:
Router lifetime (sec)
Reachable time (ms)
retrans timer (ms)
ICMPv6 Option for The source of the RA
ICMPv6 Option for the MTU
ICMPv6 Option for the /64 prefix
There are 6 flags within the flags field:


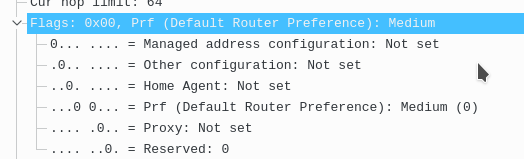
1. managed address configuration
2. other configuration
3. home agent
4. PRF (defualt router preference)
5. Proxy
6. Reserved
The default router preference is a value manually changed from medium to anything else if you have multiple routers on the segment. This will allow you to choose which router is preferred by clients. To make a router more preferred go onto it’s IPv6 interface and use
conf t
int g0/1
ipv6 nd router-preference high

Here is the wireshark results


![]()
The ICMPv6 Option for the /64 prefix features 8 fields:


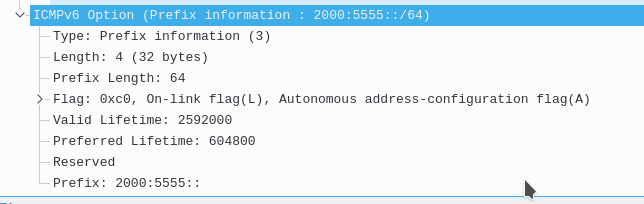
1. Type (prefix information(3)
2. Length in bytes
3. Prefix Length (/64)
4. Flags
5. Valid Lifetime
6. preferred lifetime
7. reserved
8. The IPv6 Prefix
By default routers on an IPv6 network send router advertisements for every prefix every 200 seconds
This can be changed with the interface config command
ipv6 nd ra-interval <sec>
When changing this interval, it must be less than or equal to the advertisement lifetime, so that should be set as well
ipv6 nd ra-lifetime <sec>
RAs also include network info like MTU, and hop limits
Cisco routers that run IPv6 advertise themselves as a candidate default router, meaning a gateway to clients. To disable this user the interface command
ipv6 nd ra-lifetime 0
The command above still informs hosts about the router, but it tells them not to use this router as a gateway
To completely disable router advertisements on an interface use
ipv6 nd ra suppress all
Router advertisements are also immediately sent when a router solicitation message is seen.
Router solicitation:

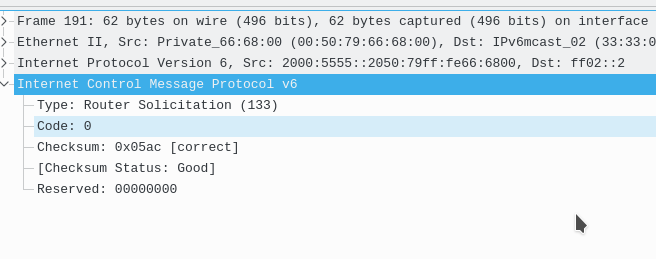

The RS ICMPv6 message features 4 fields:
Type: Always Router solicitation (113)
Code: 0
Checksum: A checksum of the ICMPv6 message
Reserved: 00000000
The router solicitation message is sent when a host or interface first comes on the network. It is used so that they do not have to wait 200 sec for the next router advertisement. Instead they just request one so they can configure themselves quickly.
neighbor redirect
This packet is very similar to the ICMP type 5 code 1 from IPv4.